Abstract
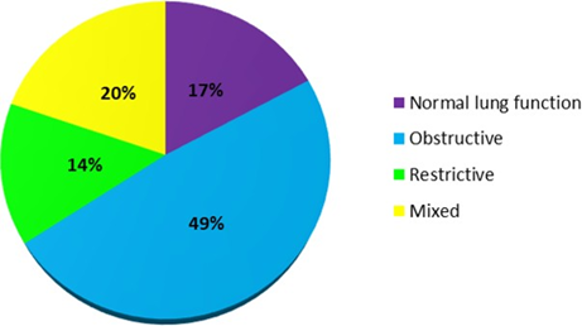
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease which has affected millions of people around the world. Ten million new TB cases were identified globally in 2018, with an estimated 1.2 million deaths. Lung function impairment often occurs due to the destruction of the lung parenchyma. This causes ventilatory abnormalities, often of obstructive type. Radiological lesions are also a common consequence of pulmonary tuberculosis. This study aims to analyse the various clinical features and assess the spirometric and radiological findings in post TB patients. This is a prospective observational study. All patients visiting the Chest Medicine OPD of Saveetha Medical College and Hospital who had a history of treated pulmonary tuberculosis and were above 18 years of age were included in this study. Patients who had no signs of active Tuberculosis underwent spirometry, and a chest x-ray was taken. Clinical presentation, spirometric parameters and radiological lesion were analysed. Among the 76 patients included in this study, 73.7% were male with most patients aged between 51 to 60 years. 64.5% of the study population were smokers. Dyspnoea (94.73%) was found to be the most common presenting complaint. Obstructive pattern (49%) was found to be the most common type of spirometric pattern with 68.42% having small airway disease. Based on the Wilcox classification, Degree II (47.37%) was the most common extent of the radiological lesion. It was found that there is a statistically significant difference between smokers and non-smokers in post-bronchodilator FEV1 (p=0.037) and FEF25-75 values (p=0.010). This study reveals the presence of post tuberculosis lung impairment in the population with varying presentations and severity. Hence, further studies and interventions are required to improve the quality of life of post tuberculosis patients.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.