Abstract
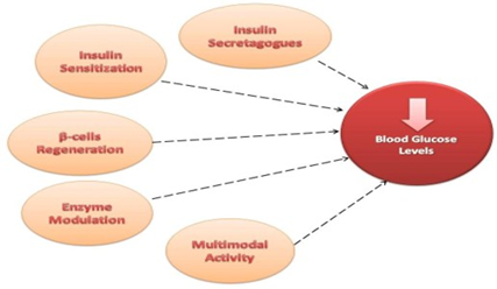
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disease that affects millions of people worldwide, described by hyperglycemia due to impaired insulin secretion, insulin action or both. As a consequence of the persistent hyperglycemia, several microvascular and macrovascular complications arise. In herbal treatments, there are quite a variety of mechanisms and pathways that could be targeted while considering the treatment of type II diabetes mellitus (T2DM); ranging from acting on pancreatic insulin, decreasing carbohydrates digestion, to inhibiting enzymes responsible for this disease like glucosidases, maltase fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase, G6Pase and PTP1B enzymes and increasing GLUT-2 and GLUT-4 translocation. There is a diverse amount of plants that have individual active constituents that are responsible for their anti-diabetic effect; such constituents belong to classes like flavonoids, phenolic compounds and alkaloids. In our review, we will report a large variety of plants and phytoconstituents that have anti-diabetic action and discuss their mechanism of action highlighting their uniqueness and thus, providing for novel targets for anti-diabetic molecules either solely or as adjunctive therapies. Ethnopharmacological studies could aid in the selection of medicinal plants to be employed in these preliminary studies. However, the exact bioactive metabolite, along with the definite mechanism of action, should be studied before experimental and clinical studies.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.