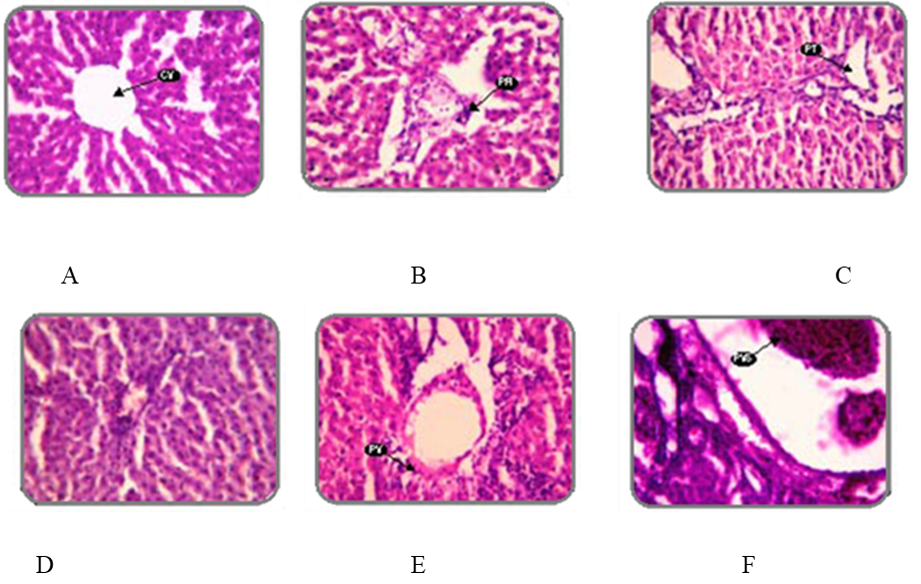
Abstract
The present study was to estimate the anti-diabetic and antihyperlipidemic activity of aqueous extract of leaves of plant Aloe barbadensis.In alloxan induced diabetes in rats, the research examined six groups of six male wister rats every to value the hypoglycaemic effect of the barbadensis (ALEC) exposed to hostile to diabetic action in rodents where alloxan monohydrates were utilized as a portion of 120.00 mg/kg in intraperitoneal portion as a diabetogenic specialist to an acquainted diabetic with test rodents. In sub intense, treatment, bunch blood glucose levels are seen on 14.00th, 21.00th and 30.00th-day present treatment compare on typical control in diabetic control checked expanded blood glucose level was watched, with dosages of 100.00, 250.00 and 500.00 mg/kg b.w. A portion of 500.00 mg/kg b.w/day was seen as having the most significant activity. Glibenclamide was applied as a standard drug, and the outcome was compared about it. In the anti-hyperlipidemic activity, serum cholesterol levels were recorded at aqueous extracts of 100.00, 250.00 and 500.00 mg/kg, on 30.00th-day post-treatment. Serum cholesterol levels were ordinary benchmark groups was 107.70 ± 01.21 mg/dl diabetic control 178.50 ± 01.04 mg/dl and standard medications treatment bunches was 111.30 ± 02.40 mg/dl and ALEC treatment bunches were 171.20 ± 01.03 mg/dl, 145.80 ± 02.92 mg/dl and 118.80 ± 03.86 mg/dl for 100.00, 250.00 and 500.00 mg/kg separately. The results show that the aqueous extract of Aloe barbadensis has significant and continuous oral hypoglycaemic activity, equivalent to the hypoglycaemic result of glibenclamide, a sulfonylurea derivative and hyperlipidemic activity. Extracts also confirmed antihyperlipidaemic possible of the plant extract is establish to be comparable with that of the standard.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.