Abstract
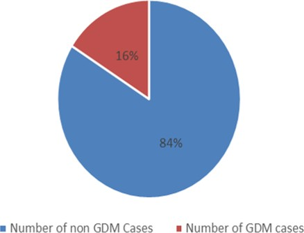
GDM is a condition in which high blood glucose level is exhibited in a women during pregnancy without a previous diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus. Indian women are considered to be more prone for developing GDM. The increasing prevalence of GDM may be due to obesity, family history of Diabetes Mellitus, sedentary lifestyle, genetic predisposition and dietary habits. The screening and management of GDM in the general population remain controversial with conflicting guidelines and treatment protocols. Adequate blood sugar control in GDM women might reduce various maternal, foetal and neonatal complications. Prospective Observational study was done to find out the prevalence and risk factors of GDM. The study was conducted in the OBG department of the study center and pregnant women with 24-28 weeks of gestation attending for antenatal care were included. The results obtained from the study says the prevalence of GDM was found to be 16% in the study center, which is at par with South Indian prevalence. This study concludes that GDM is largely associated with a family history of diabetes mellitus, obesity and higher maternal age in that particular study setup.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.