Abstract
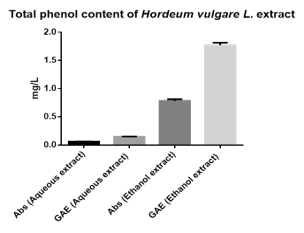
Hordeum vulgare L. (Barley) is an ancient and essential cereal grain crop with the claim that it has the potential to reduce cholesterol level and to lower oxidation activity in the liver.However, it hasn’t been proven scientifically. Hence, this study was conducted to investigate the total phenolic content (TPC), total antioxidant activity (TAC) and liver peroxidation activity of barley aqueous and ethanol extractas well as assess the effect of ethanol extract on cholesterol level of high-fat diet rats. TAC of barley extract was determined by using ABTS (2,2-azinobis-(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) diammonium salt) assay andDPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radical) assay. Meanwhile, Total Phenolic Content TPC was determined by Folin-Ciocalteu assay. A total of 15 Sprague Dawley rats were tested for the lowering cholesterol properties in barley and its association with lipid peroxidation product (Melondialdhyhe level) by adding the barley into their daily diet. The result indicated that TAC and TPC value of ethanol barley extract was high. Barley ethanol extracts effectively lowering cholesterol level in Sprague Dawley rats. Meanwhile, the malondialdehyde level in the liver tissue was a significant difference between the high-fat diet group of rats and the high-fat diet group of rats treated with ethanol barley extract. Conclusion, ethanol barley extract possess more phenolic content, antioxidant component and reducing cholesterol level of high-fat diet rats.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.