Abstract
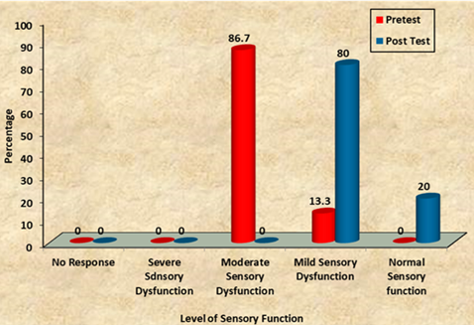
Stroke or brain attack is the effect of lack of blood circulation to the brain. Deficient blood delivery to brain results in lack of oxygen and nutrients. Brain cells are very sensitive to hypoxia. They stop working within 3-5 minutes if they are not getting oxygen and nutrients. This cell death results in stroke. Stroke is a medical emergency. Immediate treatment can reduce injury to the brain and possible complications. About half of stroke patients experience the ill effects of the problem of awareness with such antagonistic impacts as tangible hardship. The arrangement of a consideration program comprising of straightforward and safe incitements can forestall tangible hardship and improve the patient’s sensory capacity. Hence the study aimed to assess the effectiveness of sensory stimulation on the sensory function among patients with stroke. Pre experimental design-One group pre and post design was adopted for the study with 30 samples which matched the inclusion criteria were selected by non-probability convenience sampling technique. Demographic variables data were collected by using a multiple-choice questionnaire followed by assessing the sensory function by using the SMART scale. The findings of the study Out of 30 samples in the experimental group, 26 (86.7%) had moderate level of sensory dysfunction and 4 (13.3%) had mild level of sensory dysfunction. After giving the intervention of sensory stimulation post test shows 24 (80%) had mild level of sensory dysfunction and 6(20%) had normal sensory function. Sensory stimulation is effective and the patient with sensory function among stroke. This study indicates that sensory stimulation which containing certain stimulation was an effective, inexpensive, simple measure for improving sensory dysfunction among patients with stroke.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.