Abstract
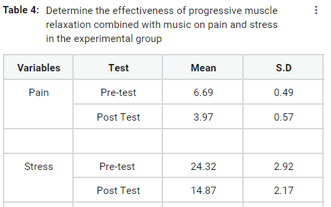
Acute pain is an often unpleasant experience during the postoperative period after abdominal surgery causes diminish in physical functioning, which evokes stress. Hence, the study aimed to determine the effectiveness of Progressive Muscle Relaxation combined with music on the reduction of postoperative pain and stress among patients who have undergone abdominal surgery. The quasi-experimental research design was chosen to conduct the study with 40 samples matched with inclusion criteria. Samples were allocated into the experimental group (n=20) and control group (n=20) by convenience sampling technique. A pre-test was done by using a numerical pain scale and the perceived stress scale for both experimental and control group. The experimental group received progressive muscle relaxation for 10 minutes, followed by theme music for 5 minutes twice a day for three consecutive postoperative days. Control group received the routine care of the hospital. Posttest was done at the end of the third day for both experimental and control group using the same tool. There was a highly statistically significant (p<0.001) reduction in the level of pain and stress after Progressive Muscle Relaxation combined with music at the level of was observed within the experimental group and also found significant (p<0.001) difference between the experimental and control group by unpaired t-test. The study results concluded that progressive muscle relaxation combined with music is useful in the reduction of pain and stress. It is also a simple, cost-effective, and non-pharmacological method that can be used to complement pharmacological management during the postoperative period.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.