Abstract
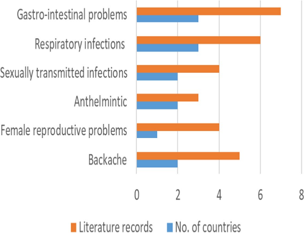
Markhamia zanzibarica (Bojer ex DC.) K. Schum.has been used in herbal medicine in tropical Africa since ancient times. Markhamia zanzibarica is indigenous to central, eastern and southern Africa. This extensive literature review synthesizes the information currently available on the medicinal uses, phytochemistry and biological activities of M. zanzibarica. The University library and electronic search engines Google Scholar, Scopus, Web of Science, ScienceDirect and PubMed were searched for pertinent information on the medicinal uses, phytochemistry and biological activities of M. zanzibarica. Traditionally, the species has been used as anthelmintic, and traditional medicine for backache, female reproductive problems, sexually transmitted infections, respiratory infections and gastro-intestinal problems. In vitro studies have confirmed the biological activities of M. zanzibarica which include antibacterial, antimycobacterial, antioxidant and cytotoxicity. Various phytochemicals such as alkaloids, anthraquinones, fatty acids, flavonoids, glycosides, phenolics, saponins, sterols, tannins and triterpenes have been isolated from M. zanzibarica. Documentation of the medicinal uses, phytochemistry and pharmacological properties of M. zanzibarica is essential as this information provides baseline data required for future research and development of health-promoting and pharmaceutical products. However, further pharmacological studies including phytochemical, toxicological, in vitro and in vivo experiments are needed to provide evidence for the clinical effectiveness of remedies prepared from the species.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.