Abstract
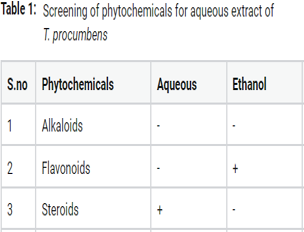
The plants are producing different types of secondary metabolites and are employed either indirectly or directly in the pharmaceutical industries. The chemical constituents of secondary metabolites improve the primary health and physiological activity in human systems. Tridax procumbens is belonging to Asteraceae family. T. procumbens is classified as a weed. In traditional medicine, the leaves, root, and stem of T. procumbens were used to treatment of stomach pain, diarrhoea, colds, inflammations, hepatopathies, bacterial and skin infections. The main objectives of present study were to screen the phytochemicals and antimicrobial activity of aqueous extract of weed plant (T. procumbens). The phytochemical screening was carried out using the stranded methods. The evaluation of antimicrobial activity for aqueous extract of T. procumbens was done by agar well diffusion method using bacterial and fungal pathogens such as Bacillus subtilis, Escherichia coli, Fusarium oxysporium and Trichoderma reesei. All the phytochemicals such as carbohydrates, phenolic groups, glycosides, tannin, alkaloids, saponin, flavonoids and steroids were present in the extract of T. procumbens and were confirmed by phytochemical analysis. The aqueous extract has not shown antibacterial and antifungal activity against tested pathogens. Other evaluation process is to be done on isolation of phytochemicals and chemical structure determination of bioactive compounds.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.