Abstract
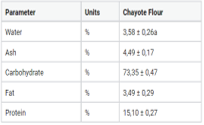
The composition of biomolecules on the squash is affected by the processing, so that the squash that have been processed into flour has a different composition, so that need for their exploration squash flour composition. This study was designed to evaluate composition of proximate, minerals and vitamins in squash flour. Analysis of proximate, vitamins and minerals using AOAC method. The percentage of ash content, carbohydrate, fat and protein respectively are (4.49 ± 0.17), (73.35 ± 0.47), (3.49 ± 0.29) and (15, 10 ± 0.27). The levels of vitamins star from the highest is a vitamin C (11.900 ± 1.072), vitamin A (0.038 ± 0.002) and vitamin E (0.015 ± 0.00007). While the mineral minerals content star from the highest is potassium (2311.90 ± 309.15), calcium (271.5 ± 9.19) and Sodium (21.69 ± 8.53). Chayote is suitable processed into flour that has the highest nutritional value of carbohydrates of 73.35 g/100 g, vitamin C of 11.9 mg/100 mg and potassium mineral of 23.11 g/100 g, so that the processing of squash flour is an innovation in the development of products made from it.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.