Abstract
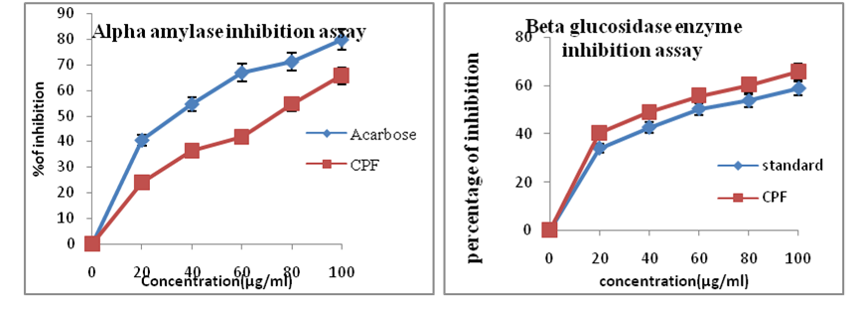
Quantitative and qualitative analysis of different phytochemical components and antioxidant and antidiabetic activities of the extract of Clerodendrum paniculatum flower (CPF) were analyzed in vitro. Chromatographic identification of phytocompounds of Clerodendrum paniculatum flower was also identified by GC-MS analysis. To assess the biochemical features of CPF. Sequential solvent extraction of CPF was performed using solvents in increasing order of polarity (petroleum ether, chloroform, ethyl acetate, ethanol, and water) and solvent with maximum phytochemical profile was standardized for further analysis. Quantitative analysis of selected secondary metabolites like tannin, flavanoids, alkaloids, and phenols of the flower extract was done by UV spectrophotometer. In vitro antioxidant assays and in vitro antidiabetic efficacy of the flower extract were analyzed by respective in vitro assays. Chromatographic identification of phytochemicals in CPF was identified by using GC-MS analysis. Quantitative estimation revealed an accountable amount of secondary metabolites like phenols (47.66mg/g gallic acid equivalent), flavonoids (24mg/g quercetin equivalent), tannins (41mg/g catechine equivalent), and alkaloids (1.79mg/g of extracted plant material). Chromatographic analysis (GC-MS) also confirmed convincing bioactive compounds in the extract. From in vitro antioxidant and antidiabetic assay, the IC50 value of the extract of CPF was measured and compared with standard, and from the results, it was evident that the extract had significant in vitro antioxidant and antidiabetic activity. From the above results, it can be confirmed that CPF has got pharmacologically significant phytoconstituents and therapeutically active ingredients, as evident in chromatographic analysis.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.