Abstract
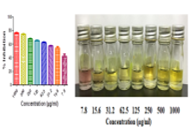
Mangiferin is a xanthone glycoside, naturally isolated from Mangifera indica. Mangiferin has been reported for a wide range of pharmacological activities and its anticancer potential is very well known. However, the mangiferin anti-cancer potency is inadequate due to its poor water solubility. N,O-Carboxymethyl Chitosan (N,O-CMC) is a smart biopolymer, in which its biocompatible, biodegradable and non-toxic making it ideal for abundant biological applications include the delivery of lipid soluble drugs. Also useful to improve and replace biological tissues and gene therapy. Hence, this study attempts to synthesize and characterize mangiferin-N,O-CMC nanoparticles and evaluate its antioxidant and cytotoxic properties. The mangiferin-N,O-CMC nanoparticles were prepared by loading mangiferin into N,O-CMC nanoparticles and characterized by FT-IR, DLS, SEM, Zeta potential and XRD measurements. In-vitro antioxidant was carried out by the DPPH method. The synthesized mangiferin-N,O-CMC nanoparticles with particle size ranges from 200±10 nm. The charge of N,O-CMC nanoparticles were confirmed by Zeta potential and found to be −45.8 mV. In the DPPH method, mangiferin-N,O-CMC nanoparticles showed IC50 value between 7.8-15.6 µg/ml. In MTT assay, mangiferin-N,O-CMC nanoparticles exhibited a significant reduction in the growth of osteosarcoma MG-63 cells and there is no toxic effect against normal 3T3 cells. These findings designated that the synthesized mangiferin-N,O-CMC nanoparticles were very efficient nanocarrier in delivering the mangiferin to cancer cells.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.