Abstract
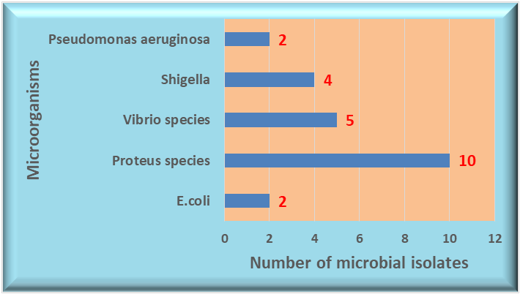
Drinking water contamination at the level of storage points poses a potential threat to the hospital environment as it can lodge some resistant pathogenic microorganisms that may cause hospital acquired infections. The study analyzed the physico-chemical and microbiological parameters of drinking water samples collected from the main water storage points from ten different local hospitals in and around Visakhapatnam using standard protocols. The samples were processed within 2 hours after collection and the identification of pathogenic bacteria was performed through Most Probable Number (MPN) method, cultural characteristics and biochemical reactions. Antimicrobial susceptibility test was carried out by Agar well diffusion method according to Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) guidelines. In the current study, all the tested ten water samples cross the permissible MPN count indicating that the water samples were not potable for drinking purpose and needs further and better disinfection procedures. Among the isolated pathogens, Pseudomonas aeruginosa exhibited highest sensitivity to antibiotics imipenem (50%) and tetracycline (50%) and resistance towards other tested antibiotics, whereas E.coli showed 100% susceptibility to imipenem and 100% resistance to ampicillin. Out of ten isolated strains of Proteus species, majority have exhibited 80% resistance to ampicillin and Tetracycline and 80% sensitivity to imipenem. All the four isolated strains of Shigella species expressed 100% resistance to ampicillin and 75% sensitivity to imipenem, meropenem, azithromycin, linezolid, vancomycin and chloramphenicol. The five isolated strains of Vibrio species showed 100% resistance to ampicillin and 80% sensitivity to imipenem, doxycycline and tetracycline.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.