Abstract
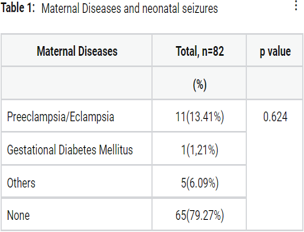
Seizures are common neonatal illness amongst neurological disorders. The study was conducted to determine the clinical profile of neonatal seizures. A hospital based prospective observational study was undertaken in the NICU of a rural set up in central India. A total of 82 neonates admitted with seizures or who developed seizures later during the stay in NICU were subject population of the study. Of 82 neonates with seizures, the overall mean for duration of stay was 14.34 (±10.41) days and the interquartile range was 1-32 days and male predominance. Majority of neonates included were extramural deliveries (62.19%). The distribution of neonates in the study according to their gestational age, birth weight, route of delivery & MSAF was found to be statistically insignificant (p Value >0.05). The vaginal route of delivery was more common than the caesarean section among neonates with seizures in the study. The overall mortality rate was 17.07% (14/82). In most of the cases, the causes of neonatal seizures were present. Birth asphyxia was the main etiology identified. The antenatal services and intrapartum monitoring is important.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.