Abstract
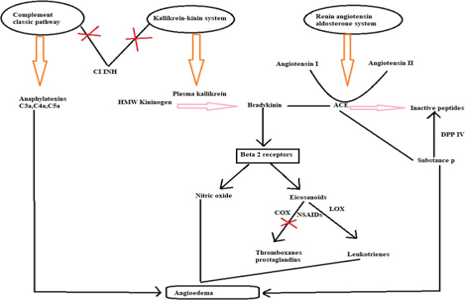
Non- Steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are among the most commonly prescribed category of drugs. NSAIDs are the main cause of allergic reactions both in adults and children. Hypersensitivity reactions due to NSAIDs involve 0.3% to 0.5% of the overall population. Among the different types of NSAIDs induced hypersensitivity reactions, urticaria and angioedema are the most common. Angioedema can be of two types, allergic(IgE) & Nonallergic (Non IgE) mediated. Allergic angioedema is immune mediated but non allergic angioedema mimic immune mediated allergic reaction without underlying evidence of immunological mechanism which can cause diagnostic difficulties for the clinician. Distinguishing immune-mediated and non-immunemediated reactions can be difficult, so careful evaluation is needed. Pathomechanism of NSAIDs induced non allergic angioedema is based on cysteniyl leukotrienes and bradykinin pathway in which NSAIDs block cyclo oxygenase pathway and directs the lipoxygenase pathway and generates leukotrienes which result in the development of angioedema. NSAIDs induced allergic angioedema is quite frequent and NSAIDs induced nonallergic angioedema are quite rare. The detailed information of these reactions is necessary to decrease morbidity and mortality associated with the reactions. The early recognition and discontinuation of suspected drug should be done in order to avoid further complications. Here, we report a case of a patient with non allergic angioedema in association with use of Ketorolac.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.