Abstract
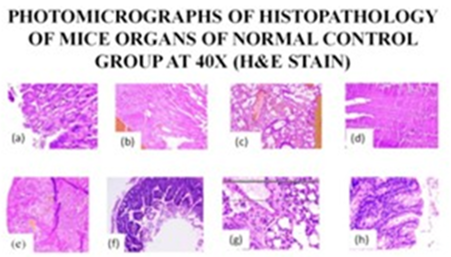
Acute and subacute toxicity screening of novel entrants in the stream of polyherbal formulations opens new doors towards the scientific approach of establishing them in the clinical market. Toxicity profiling asserts the humongous pharmacological potential that the natural herbs hold and establishes their safety profile. To exemplify this statement, this study further deals with acute and subacute toxicity studies of an olive oil-based polyherbal combination (PHC). This combination has been developed with the view that it proves to be clinically effective in diabetic cardiomyopathy and neuropathy. However, until now, the acute and subacute toxicity studies have been done on the developed PHC, and experimentally effective dose combinations have been identified. The follow-up part of this research includes the screening of the PHC against specific in vivo screening models in its initial stages. This research paper strictly summarises the acute and subacute profile of the salubrious polyherbal combination. Three herbs with strong literature background were selected: Tinospora cordifolia, Withania somnifera and Boerrhavia diffusa; and their crude extracts were prepared. The reported ED50 values of each of these plants were selected and mixed in 5 different combinations and subjected to Acute Toxicity studies. It was followed by the 28-days subacute toxicity screening of 9 different combinations that were elucidated from the acute toxicity study results. The findings were supported with recovery group studies to conform to any late toxicity symptoms of the polyherbal combination. The findings of this study helped in reaching some pathbreaking conclusions on the polyherbal combination designed.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.