Abstract
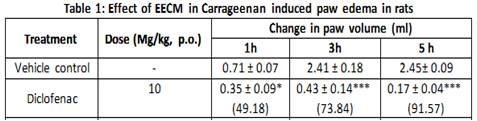
The present study was to evaluate anti-inflammatory activity of ethanolic extract of root bark of Crataeva magna Lour (DC) (EECM) at 100, 200 and 400 mg/kg body weight was studied for anti-inflammatory activities in different animal models. Anti-inflammatory activity was carried out by using carrageenan induced paw edema model and cotton pellet induced granuloma model in wistar rats. The anti-inflammatory activity may be due to presence of Phytochemical compounds present in the extract like alkaloids, flavonoid, triterpenoid, phenols, saponins and tannins. The results suggested that EECM possess anti-inflammatory activity in (200 and 400 mg/kg) also showed significant (p<0.001) anti-inflammatory activity by reducing the paw edema volume in carrageenan-induced paw edema in rats in the late phase (3 to 5 h) regulated by prostaglandins and leucotrienes and in cotton pellet induced granuloma model EECM decreased dry weight of granuloma. The effect was also comparable to Diclofenac, the standard drug in this study.
Full text article
Generated from XML file
Authors
Meera R, & Venkataraman S. (2023). Evaluation of anti-inflammatory activity of Crataeva magna Lour (DC) root bark in experimental animals. International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences, 8(3), 415–419. Retrieved from https://ijrps.com/home/article/view/4596
Copyright (c) 2017 International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.