Abstract
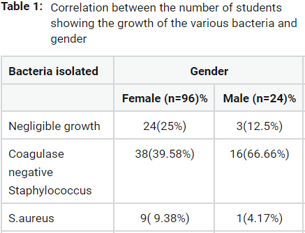
Human skin is a complex ecosystem with various microenvironmental conditions and thus, the presence of resident microbial flora prevents colonization by pathogens. Some cosmetics like skin peels are known to cause deeper exfoliation of the skin and causes loss of skin flora. So, in the present study, the attempt was to find out the effect of cosmetics that are applied to the face on resident flora of the face of medical students who are exposed to the hospital environment. Out of 120 subjects, 60 were cosmetic users and 60 were non-cosmetic users. Swabs were collected from the face of subjects after washing the face with soap and water and processed using standard techniques. The colonies were counted, identified and statistically analyzed. The isolated colonies were Coagulase Negative Staphylococcus (CoNS), Staphylococcus aureus, Micrococcus species, gram-negative bacilli and Corneybacterium species from both the groups. It was found that regular cosmetics users 12(20%) yielded less isolates of CoNS as compared to non-cosmetic users 42(70%). It was found that the use of cosmetics thus decreases the normal resident flora of the skin, but larger studies with more subjects are needed to confirm the present result.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.